Object-Oriented Programming
Features of OOP
- OOP is a programming paradigm that uses "objects" to design applications and computer programs.
- OOP allows the programmer to create an object that combines data and functionality.
- Data often known as attributes or properties, and functionality often known as methods or behaviors.
- OOP makes it easy to map real-world problems and solutions.
OOP Concepts
- Class: A blueprint for creating objects.
- Object: An instance of a class.
- Inheritance: Reusing an already existing design to design a better object.
- Polymorphism: Doing the same thing in different ways.
- Encapsulation: Packing the data and behavior together.
- Abstraction: Focusing on what needs to be done and ignore the irrelevant aspects of the problem.
Features of C++
- C++ is a superset of the C language.
- A multi-paradigm programming language that supports procedural(can focus on distinct activities) and object-oriented(can focus on distinct objects).
- realistic, efficient, and flexible enough for demanding projects.
C++ Compiler
- A C++ compiler is an operating system program that converts C++ language statements into machine language equivalents.
Stages of Compilation
- Preprocessing: The preprocessor processes directives in the source code, such as #include for header files and #define for macro definitions, before it is passed to the compiler.
- Compilation: The compiler translates the preprocessed source code into object code in binary format.
- Linking: The linker combines the object files generated by the compiler into a single executable file.
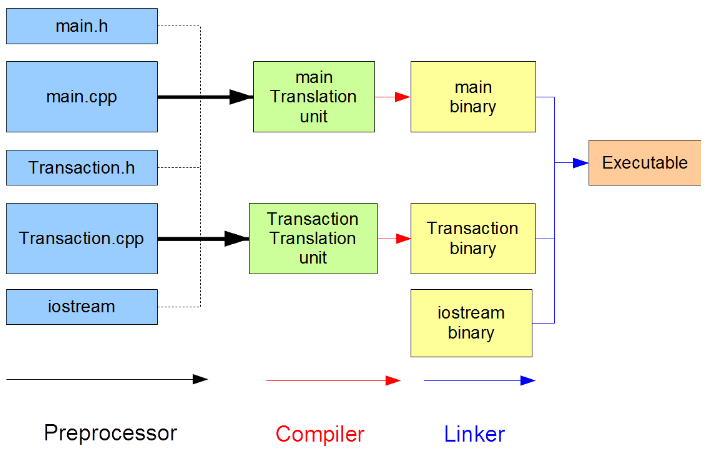 source: https://intro2oop.sdds.ca/A-Introduction/modular-programming#modules (opens in a new tab)
source: https://intro2oop.sdds.ca/A-Introduction/modular-programming#modules (opens in a new tab)
Modular Programming
- Modular programming is a software design technique that emphasizes separating the functionality of a program into independent, interchangeable modules.
- Each module contains everything necessary to execute a specific aspect of the desired functionality.
- The modules can be developed, tested, and maintained independently.
Modular Programming in C++
- In C++, a module is implemented using a header file and a source file.
- The header file contains the declarations of the functions and variables in the module.
- The source file contains the definitions of the functions and variables in the module.
namespace
- A namespace is a declarative region that provides a scope for the identifiers declared within it.
- Namespaces are used to organize the code into logical groups and prevent naming conflicts.
- The
namespacekeyword is used to define a namespace.
namespace my_namespace {
int x;
void foo();
}